What you need to know about Li-Fi

While radio-based communications technology seems to be nearing the end of its growth potential, a new technology has come up with an entirely different approach: Li-Fi. Instead of low-frequency radio waves, this technology uses ultra-high esophageal light, which dramatically increases its data transfer rate. Now let’s see what Li-Fi is?
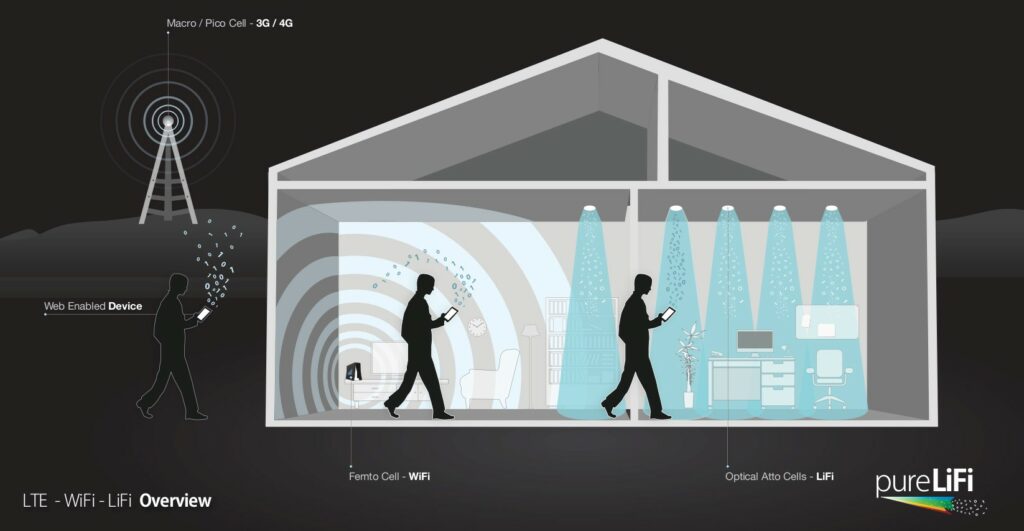
Today’s wireless networks operate within a range of wavelengths known as radio frequency or RF. Until recently, Wi-Fi networks only rely on two 2.4 and 5 GHz frequency spectra. In a new move, the 802.11ad standard adds a 60 GHz spectrum to this collection and has brought its transfer speed to 7 Gbps. But the radio frequency is ultimately limited to 300 GHz, and note that increasing the frequency in this area would mean reducing the range or vulnerability to barriers.
Now a new member of the wireless communications technologies group, called Li-Fi (Light Fidelity), that employs a completely different approach is opening its way into the commercial products field. Li-Fi is a Visible Light Communications (VLC) technology, which means it uses light to transmit data.
If the whole idea of this technology sounds a bit strange to you, it is not bad to know that visible light deals with frequencies ranging from 300 to 800 terahertz. Compare this number to the RF frequency range to determine the Li-Fi potential. If you want to get some figure, the researchers at Oxford University have managed to reach 224 gigabits per second through this technology. This is the equivalent of transferring 28 gigabytes per second, which will be enough to download 10 HD movies in just one second.
How does Li-Fi work?
As we said, Li-Fi relies on transmitting information by visible light. At present, only LED lights can be used for Li-Fi communications. LED is a semiconductor structure that emits light, so its input current can be increased or decreased at very high speeds that are not recognizable to the human eye. As you guessed, this process can create light pulses which information is transmitted through them.
On the other side, there will be a photodiode sensor that detects this light pulse and thus receives information. Very fast and small changes in the brightness of the LED on the receiving side is converted to electrical signals and then binary data, just as when you receive them through a Wi-Fi connection on your system.
Advantage of Li-Fi
– Extremely high speed with low power consumption
– Li-Fi uses visible light, so there will be no interference with the extensive range of gadgets that surround us today and use RF waves (Wi-Fi-compliant devices, mobile devices, wireless phones, keyboards and wireless mouse, etc.).
– A Li-Fi connection requires a direct line of sight to work, so only when the user is in the light domain of the transmitter’s LED, it is possible to communicate with a LiFi network. In this way, no one can connect to the network without your awareness.
– The light does not cross the same walls and obstacles, so when you use a LiFi-based network in your home, for example, no one outside the walls of your home will be able to penetrate your network.
– Because of its work structure, Li-Fi does not pose a risk to users’ health.
– Installing and setup of Li-Fi is very easy.

Disadvantages of Li-Fi
– You will receive information only as long as you are in the transmitter’s LED light range.
– Other bright light sources, may interfere with your communication signal.
– Li-Fi is not compatible with the existing network infrastructure, and you need to have the completely new equipment to use.
As you can see, Li-Fi, like every other technology, faces various challenges and has many advantages and disadvantages. However, the data rate potential of this technology can justify the efforts focused on it. Li-Fi is still far from becoming a public commercial technology, but with the introduction of prototype products that use this technology, it does not seem to take long for users to take advantage of its capabilities.


